Shopping centres
Heart of Europe Stifling Under Concrete:The construction boom of shopping centres in Prague
Foreword
The Shopping Gallery Harfa opened in November 2010. The Fenix Shopping Gallery opened in 2008. They both lie at a driving distance of approximately 5 minutes from the biggest shopping area in Prague and the Czech Republic - OC Letňany built in 1999. I visited Fenix on the 23rd December 2010 and it felt like ghost town. And on one of the busiest days of the year! This experience made me wonder, how it is possible that energy and resources are wasted on redundant chapels of consumption. In the Czech Republic the so-called area standard – square metres of shoppin space per inhabitant – has tripled since 1989 from 0,331[1] to 1,1 in 2009[2]. That means that every citizen in this country has their own square metre for shopping. Of this, shopping centres represent 0,26 m2 per inhabitant(sq/inh)[3]. Compared to Liberec for example, which has a value of 1,4 m2/inh[3], Prague might seem quite empty with its 0,72[3]. The frequency of new shopping centre openings, however, challenges common sense. Prague is fancied for its intimacy and was honoured by becoming a part of the UNESCO world heritage site in 1992 thanks to its historical value. The construction boom is sometimes acused of threatening the town´s uniqueness. Sýkora (2006)[4] warns that new investments after 1990 contributed to densification of central city morphology including rapid growth in car traffic and consequent congestion, which turned out to be especially critical in Prague. Furthermore Sýkora adds that there have been numerous conflicts between investors and those protecting historic buildings and urban landscapes. Another argument in the discussion is environmental sustainability. As the Prague City Development Authority Prague points out, developing commercial areas significantly increase the proportion of built-up land and so opportunities for establishing adequate proportions of greenery descrease. Numerous civic petitions for maintaining parks or other free land in different parts of the city have been signed.
I will take a closer look at the situation of shopping centre construction in Prague and try to find out, what is happening and where the problem lies.
About shopping centres in general
Shopping centres have been replacing traditional markets since the last century. They represent the modern lifestyle as they are sometimes called the chapels of consumption. I. Smolová[5] provides an overall definition(translated): “A Regional Shopping Centre is an architecturally unified complex of commercial facilities planned, constructed, owned and administered as a whole. They represent a concentration of retail stores, catering and services (entertainment and cultural establishments, e.g. multiplex cinemas) aiming to satisfy the customers’ requirements in the field of goods and services in a short-term, mid-term and long-term perspective. The basis of shopping centres is formed by big retail units of the hypermarket type and by specialised superstores (e.g. hobbymarket).”
The localisation of shopping centres is determined mainly by the proximity of potential customers and accessibility by transport. Given the ratio of sales area to total required area stands at approximately 1:7[5], the localization is limited by the availability of development areas and by lot prices. In relation to Prague, the most sought-after places are on the edges of the city and its high streets.
Shopping centres in the Czech Republic with a focus on Prague
Shopping centres did exist before 1989 – every citizen then knew the famous first western-like Kotva Retail House for example. Nevertheless the massive expansion of this shopping phenomenon began after the revolution in 1989 as a result of joining the global market. Prague being the capital city forms a kind of bridge between the national and foreign market and therefore it has been the most affected globalisation and internationalisation. The service sector has grown rapidly whereas industry was left behind, which resulted in the existenceof brownfields in several areas. The most visible recent urban tendency is suburbanisation including outward migration and commercialisation. Stores, logistic centres and shopping areas have been built. As I mentioned in the foreword, the area standard of Prague has the value of 0,87 m2 per citizen. The total number of shopping centres in the capital is 38, their area present 33% of the national shopping centre area (CBRE, 2010).
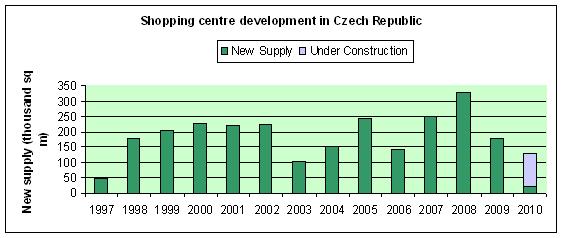
Fig. 1: Shopping Centre Development in The Czech Republic, CBRE (2010)[3]
Figure 1 shows that shopping centres experiencied a steep increase in construction in the year 1998. The peak was in 2008, which is the year of opening of big Prague shopping centres like Arkády Pankrác (40 000m2) or the afore mentioned Fenix Gallery (12 000m2). Most of the new construction was located in smaller towns however - the focus of investors moved out of cities to these less saturated regional towns. [6] The graph shows there has been a decreasing tendency in the last two years. In 2010, the financial crisis was manifestated in construction perhaps even more than in others fields, as only one shopping centre opened in Prague(Harfa Gallery).
Legislation
Three main laws are relevant to the topic of shopping centre construction in the Czech Republic: firstly The Construction Act No.183/2006 Coll.; secondly, Act No.334/1992 Coll. on Protection of Agricultural Soil; and lastly Act No.100/2001 Coll., containing Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). These include the general principles of the building processes, the conditions of use of agricultural soil for other than agricultural purposes and the criteria for EIA (for example, since 2007 projects with less than 3 000 m2 and fewer than 100 parking spaces can be omitted from the EIA). Complex regulations concerning specifically big shopping centres are missing though.
Policy and Planning
In the Czech Republic, the responsibility for policy making rests primarily with municipal governments. The problem is that the so-called functional urban region extends the political boundaries of the core cities. In regard to Prague it is surrounded by over 170 small municipalities which are economically and legally independent units and whose decision-making process lacks wider coordination. Moreover, the metropolitan area of Prague is governed by two overlapping local body entities – Prague itself and Central Bohemia which tend to compete rather than cooperate on the question of joint development.
Prague itself, as a statutory town, has its municipal territory divided into 57 boroughs, therefore establishing a second tier of local governments which takes advantage of the gained partial autonomy in decision making. However, they ought to respect two citywide planning documents – The Master Plan and The Strategic Plan. The former is a physical plan that specifies the special arrangements and land use in the medium term, while the latter specifies the long term priorities of socio-economic development.
The Strategic Plan specifies controlled development and coordinated management and decision-making in order to achieve prosperity, a healthy and cultural environment, and the preservation of values which make Prague one of the most beautiful cities in the world. It is an agreement between politicians, specialists, corporate sector representatives and inhabitants. One of the five pillars focuses on the quality of the environment: “Prague endeavours to achieve a high quality of both natural and urban development, while observing the principles of sustainability. It wants to substantially reduce pollution in the city and create balance between human settlement and landscape in order to become a clean, healthy and harmonious city[4].” Besides these two documents, Prague has worked on policies in accordance with the EU demands and has created a Regional Development Strategy which basically matches the Strategic Plan.
A feedback on the current policy
In this part, a resume of a feedback document - Planning Analytical Materials [7]- carried out by the City Development Authority Prague in 2008 is provided:
The ongoing pressure on building new shopping centres and office complexes is seen as a threat to the lively metropolitan structure and to the transport network. The new European trends is to mix compact construction with lower capacity facilities. Newly constructed and reconstructed big capacities of retail outlets and offices, such as the newly opened Palladium complex, place emphasis on traffic because of parking demands and with their 100% built-up land they limit areas for new parks or greenery for the relaxation of local inhabitants and workers. Due to greater interest in ing in shopping complexes the survival of existing parks in the Prague city centre is endangered as well.
A negative trend is the low support of the private sector in mettinf the financially less attractive functions of the city, which includes public facilities, greenery and recreation areas. There is also a mismatch between customer interest in traditional dispersed retail networks and the new fashion for travelling to big shopping centres on the outskirts of Prague which generates traffic congestion and so causes damage to the environment.
A problem solvable by the Master Plan is insufficient coordination of store and logistic areas in the city surroundings. What is beyond the competences of the plan, however, is regulation of retail network in favour of smaller units, as well as the pressure of economic land use at the expense of urban aspects and environmental protection.
The Planning Analytical Materials of 2008 recommend that no more land is dedicated to big shopping centres except for newly proposed district centres.
Problems connected to commercialization – urban, environmental and social aspects
The existence of shopping centres definately brings several benefits to society. These can be employment, shopping availability, economic growth. However numerous unpleasant consequences of the contruction of shopping centres have been observed. A list of the most important ones follows.
1. The question of population decline in the city centre emerges as more and more buildings are loosing their residential function and used for office or retail areas instead. 2. As a result, people move out of the centre but commute there to work or for shopping, which causes traffic congestions. Suppliers contribute as well.
| trafic increase | number of retail units | rate |
|---|---|---|
| < 5% | 66 | 26,50 % |
| 5,00-9,99% | 67 | 26,90 % |
| 10-19,99 % | 65 | 26,10 % |
| 20-29.99 % | 28 | 11,20 % |
| > 30% | 23 | 9,20 % |
| total | 249 | 100 % |
| average | 11 % |
Fig. 2: The impact of retail construction on traffic, NESEHNUTÍ [8]
This chart provides a dividing of retails units by the precentage of traffic increase that appeared after the opening. The good perception might be than 1/4 of the cases registered an increase of 5% in maximum. On the other hand the same number of cases reported an increase of up to 20%, which might be a horour for infrastructure in case it was often congested already. Increased traffic is a burden not only for the air quality, but also worsens noise pollution (currently one of the worst problems of the Czech environment) and throttles pedestrian comfort and safety too.
3. At the expense of new construction investments the already rare greenery is diminishing in the city centre.
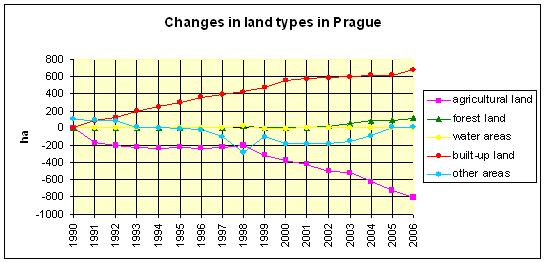
Fig. 3: The development of different types of land in Prague, ENVIS[9]
Eventhough politicians like to pride themselves with numbers of newly planted trees or hectares of newly set up urban greenery, this chart shows that in total the nature-like land (forest, water, agricultural and other areas) has more or less stagnated, whereas the built-up area has increased has risen significantly since 1990.
4. Construction of suburban SC occupies land even more, because roads and parking lots have to be built too. Traffic increases again. A research from EIA 2003-2009[8] shows that
- 72% of SC in the Czech Republic have been built in the suburbs
- Buildings take up 30% of the construction lot, roads and parking lots 45%
- 92% of parking sites have been designed as surface types, the rest as underground or inside
- One half of SC have been built upon green fields, 10% of that land being the I. category agricultural soil intended to be built upon only in the most special cases.
- 46% of SC have had a negative effect on landscape (soil degradation, tree cutting, endangering ecological stability etc)
5. Small, former retailers are threatened and see SC as “unfair rivals”.
6. The design of new SC often omits local urban patterns and so interrupts the landscape or even the historical values. A study[10] on this topic claims these factors:
- A trend of globally active artist creating international images of cities has emerged, buildings are designed to show global success as a part of the marketing strategy of their owners. This means that the architecture is becoming rather unified, local specific manners are omitted often and so one can observe the same designs worldwide. Example images, both from abroad and Prague are shown to prove the theory (pictures taken from Wikipedia Commons):
 Entertainment centre Černý Most, Prague, Czech Republic
Entertainment centre Černý Most, Prague, Czech Republic
- New projects engage foreign investors, which reflects in their names (Anděl Bussiness Center), in the similarity of financing (the developer designs the exterior x the client chooses the interior composition) and in construction similarity. A new type of construction occurs, it is the so-called groundscraper model. A grounscraper takes the american way (skyscraper) of construction but adjusts it to european conditions. It is a horizontal building fulfiling a whole block and besides offices it includes other functions - shopping, entertainment, food. The concept can be illustrated by pictures from Wikipedia Commons:
 Shopping centre Wakamatsu. Fukuoka, Japan
Shopping centre Wakamatsu. Fukuoka, Japan
 Galerie Butovice, Prague, Czech Republic
Galerie Butovice, Prague, Czech Republic
 Shopping centre Letňany, Prague, Czech Republic
Shopping centre Letňany, Prague, Czech Republic
 Centrum Chodov, Prague, Czech Republic
Centrum Chodov, Prague, Czech Republic
- Especially suburban stores and SC express rationality and purpose of machines of mass consume and create an atmosphere of a placeless city
Conflict
Citizen NGOs were probably the first to start complaining about retail construction as it has affected the direct surrounding of their homes. A good example is an NGO called Healthy Life founded in 1998 in Prague 10 in order to protest against the construction of SC EDEN, located close to the Slavia football pitch. As their website[11] claims, this SC was built despite the lack of necessary approvals. This NGO and other bodies appealed against the Prague 10 Council´s permission of the construction and even though the Supreme Court decided that the decision-making process had been wrong and must start again (and so the building permit is invalid), the investors started cutting trees and building engineering network. Later on there was not enough power on the side of opponents to stop the construction.
The most important arguments of Healthy Life were that the park, which lay on the allotment was the only green land in a wide area and that the construction of a SC would increase traffic and worsen air-pollution.
Images from Wikipedia Commons follow:
 The development of Eden shopping centre, Prague, Czech Republic
The development of Eden shopping centre, Prague, Czech Republic
 Eden shopping centre, Prague, Czech republic
Eden shopping centre, Prague, Czech republic
Another example is the Pankrác Plain with SC Arkády, an area where skyscrapers have been built and a big discussion rose about a threat of UNESCO punishment (because the skyscrapers might disrupt the city’s panorama). Again and NGO was founded and a dispute went on. Citizens always refer to the EIA process because it is their only legal possibility of joining the discussion. They hope the EIA results might cause fatal trouble to the investor, but all the cases show that this political/environmental instrument is not powerful enough to actually stop a whole project.
Media have supported every now and then the fragmented citizen efforts. Articles with for example these headlines were published: “A stamp is enough to turn a park into a parking” (Ekonom, 9.1.2003) or “Arkády Pankrác are opening, other shopping centres struggle to survive”(ČT 24, 14.11.2008) or “Shopping centres are mounting up despite the crisis” (Profit.cz, 27.4.2009).
Politicians, important actors in the conflict, are usually rather silent and not much explanations or quotations are findable. From the few comments in media I have assumed that their argumentation in favour of SC construction is of financial character, that is to say that the given city part wants to profit from selling allotments and claims SC to bring local importance and raise the economic value of the area.
As for the developers, their role is quite simple – they act as businessmen looking for profit and don’t pay much attention to other aspects.
Future development
The Czech retail structure has undergone a rapid evolution since 1989. The construction of new shops and commercial centres has been so massive that it gave an image of uncontrolled sprawl. Numbers say we have recently reached the European level as concerns the area standard (square metres of shops per inhabitant), which undermines my worries – probably there is no over-construction if it’s the same as in the rest of Europe! Nevertheless a more general question arises: is the European average a relevant measure for Prague? And moreover isn’t the current average a sign of overconsumption? These are question beyond the scope of this study case, but they definitely present a challenge for human lifestyle.
To conclude I will cite an up-to-date article from Lidové noviny (Public Newspapers, 11.1.2011). Its headline is “The dusk of huge shopping centres” and points out that in 2011 no SC will be opened (for the first time since 1990!) because the Czech Republic is saturated. This fact is a result of a market self-regulation rather than urban and political planning, but it seems that the construction boom of SC hopefully ended together with the first decade of the millennium and therefore the future development should be pretty much calmer and slower. Current trends turn back to the establishment of retail in existing buildings (eg.high streets) instead of constructing massive complexes on green fields.
Research question
During the development of my case study I have learned that the construction of shopping centres features more aspects than the ecological one I have been anxious about. Architects are concerned about the design, small traders feel discriminated, citizens complain about traffic congestions…
The most worrying matter however is the lack of effective communication in the process preceding the construction itself. Starting from insufficient cooperation between administrative organs through to the absence of specialist (architects, environmentalists) tuition and ending by limited possibilities of participation of citizens. Therefore a research question arises: Do the Czech laws concerning the decision making process posses enough control mechanisms to prevent corruption and assure equal possibilities of involvement of all affected sides?
Rerefences
- ↑ Ministry of Industry and Trade
- ↑ Incoma Research
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 CB Richard Ellis, 2010: http://www.cbre.cz/propertyinfomap/emea/_PDF/EMEA_FPR_CZECH_RETAIL%20_H1_2010_ENG.pdf
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 L. Sýkora (2006): Urban Development, Policy and Planning in the Czech Republic and Prague.I'n 'Altrock, Guntner, Huning and Peters: Spatial Planning and Urban Development in the new EU member states. Ashgate Publishing, UK
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 I. Smolová, Z. Szczyrba (2000): Large commercial centers in the Czech Republic - Landscape and regionally aspects of development. Palacky University Olomouc
- ↑ http://www.ct24.cz/ekonomika/12186-boom-nakupnich-center-se-presouva-do-regionu/
- ↑ http://www.urm.cz/uploads/assets/soubory/data/UAP/UAP_book/kapitoly/04_kapitola_4_uap_2008.pdf
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 NGO NESEHNUTÍ http://nesehnuti.cz/publikace/vyzkum_2003-2009.pdf
- ↑ ENVIS, 2007: available on-line
- ↑ J. Temelová (2004): The Reflection of Globalization in non-housing estate in Prague after 1990. In M.Ouředníček: Social Goegraphy of the Prague Region. Charles University in Prague, 2006
- ↑ available at Econet web